Explain Dataframe functions with example: head, tail , loc, iloc, value and to_numpy().
SOLUTION....
DataFrame methods: head, tail, loc, iloc, values and to_numpy() — explained with examples
Below is a short, original, and practical explanation of each method/attribute plus examples you can try in Python with pandas.
1) head(n=5)
What it does: returns the first n rows of the DataFrame (default n=5). Useful for a quick preview.
Example

2) tail(n=5)
What it does: returns the last n rows (default n=5). Handy to inspect dataset end.
Example
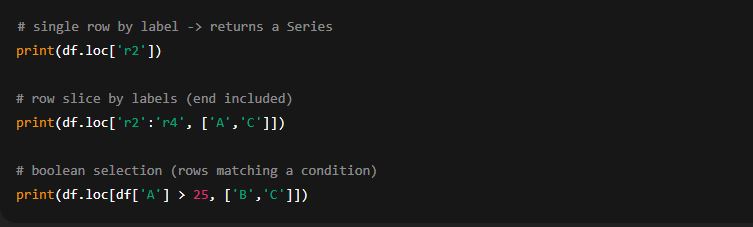
3) loc — label-based indexing
What it does: select rows/columns by label (index names and column names). Slicing with loc[start_label:end_label] includes the end_label. Works with boolean masks too.
Examples
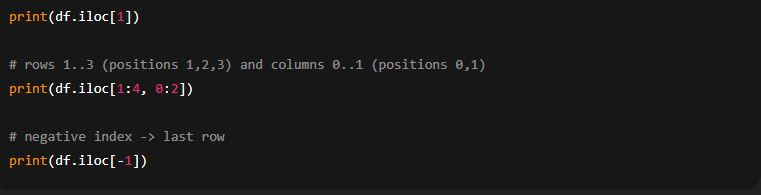
4) iloc — integer position indexing
What it does: select rows/columns by integer positions (like standard Python indexing). Slicing with iloc[start:stop] is end-exclusive (stop not included).
Examples
Key differences (loc vs iloc):
loc→ label-based (inclusive slicing).iloc→ position-based (Python-style exclusive slicing).Example: for integer index
[0,1,2],df.loc[0:1]returns rows with labels 0 and 1;df.iloc[0:1]returns only the row at position 0.
5) values (attribute)
What it is: df.values returns the underlying array-like object (usually a NumPy ndarray), containing the DataFrame data.
Example

