What is a module in AngularJS? Also explain how to create a controller of the module with an example.
SOLUTION....
What is a module in AngularJS — and how to create a controller for it (detailed)
A module in AngularJS (Angular 1.x) is a container that groups related parts of an application — controllers, services, directives, filters, configuration, and constants. Think of a module as the application’s main namespace and dependency manager: it declares what the app contains and what other modules it depends on. Modules keep code organized and make it easy to compose features or reuse code across apps.
Key purposes of a module
Organization: collect controllers, services, directives, etc., under a single name.
Dependency management: declare other modules your module depends on (so Angular injects them).
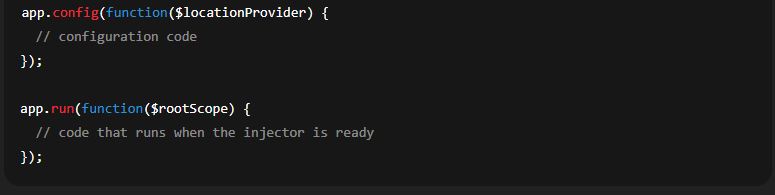
Configuration stage: provide
.config()and.run()blocks to configure providers and run startup logic.Bootstrapping: the app is bootstrapped with an entry module (via
ng-appor manual bootstrap).
How to define a module
Create a module with angular.module('moduleName', [dependencies]).

To retrieve an existing module (no re-creation), call angular.module('myApp') with no dependency array.
You can add configuration or run blocks:
Creating a controller for the module
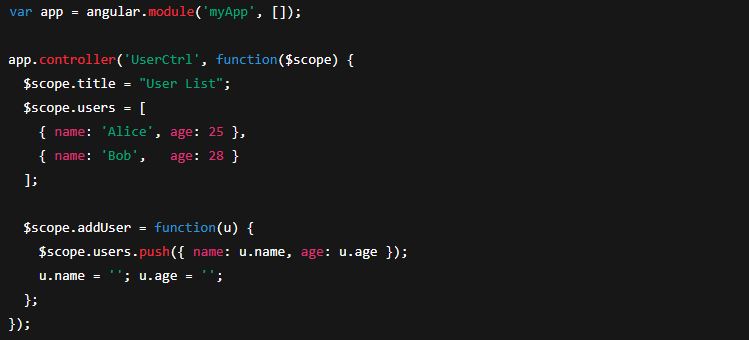
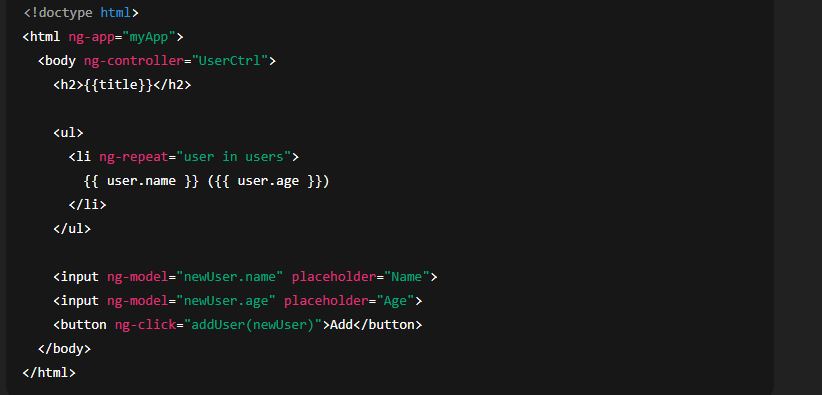
Controllers contain the logic that connects the view (HTML) and the model (data). You register a controller on the module with .controller().
There are two common styles:
1) Classic $scope style
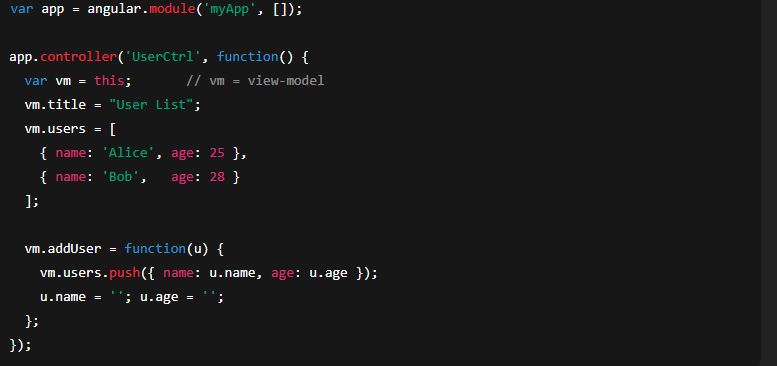
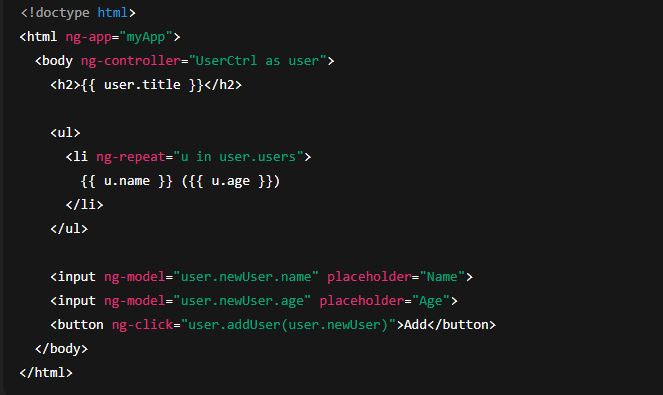
2) controllerAs pattern (recommended)
This avoids $scope for better readability and easier migration/testing. Use this inside controller and bind it to a name in the view.
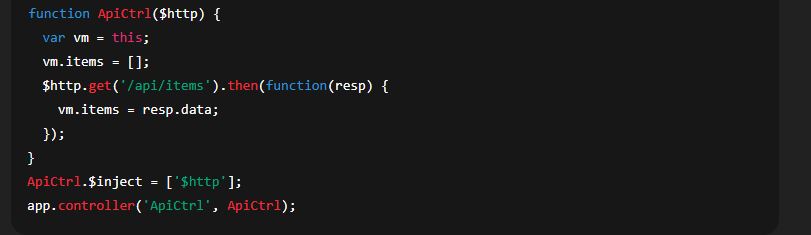
Dependency injection and minification-safe code
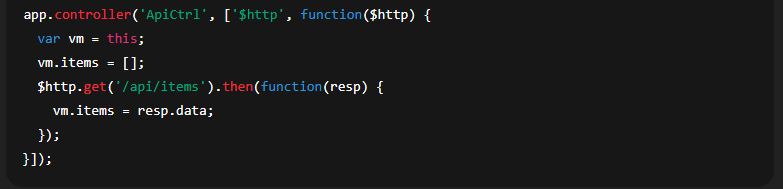
When injecting Angular services (like $http, $scope) and you minify code, you must use array annotation or $inject to keep injections safe:
Array-style annotation:
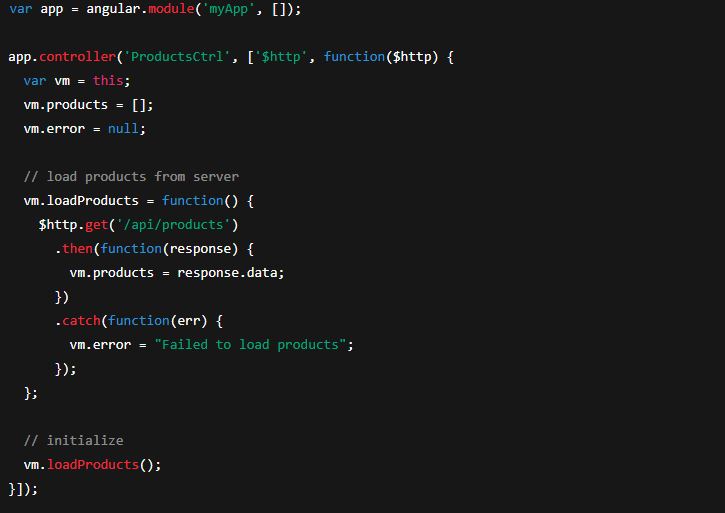
Example: Module with controller using $http (realistic)
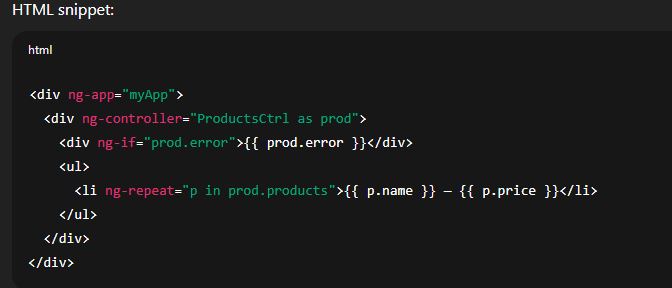
Extra module features (quick overview)
.factory()/.service()/.provider()— register reusable services..directive()— register DOM-manipulating directives..filter()— register view filters..constant()/.value()— register configuration values.
These are all attached to the same module object, so the module is the central registry.
