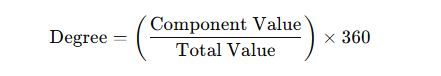Chapter 1 Graphs in Economics
Chapter 1 Graphs in Economics
Chapter 1 Graphs in Economics
Q.1 Choose the correct option for the following questions :
1.For which type of distribution a diagram is drawn?
(a) Continuous
(b) Discrete/Discontinuous
(c) Skewed
(d) Ideal
2. For which type of distribution a graph is drawn?
(a) Continuous
(b) Discrete/Discontinous
(c) Skewed
(d) Ideal
3. Which of the following diagrams are drawn for similar data?
(a) Simple bar diagram and clustered bar diagram
(b) Bar diagram and pie diagram
(c) Clustered bar diagram and time-series graph
(d) Pie diagram and time-series graph
4. Which of the following statements is true for the internet in the present times?
(a) It is a tool for studying.
(b) Fulfils the role of a teacher in the process of studying.
(c) Is a close substitute for schools.
(d) Is only a tool for entertainment for youth.
5. Who/Which type of organization presents data CDs pertaining to economic information?
(a) Private publishers
(b) Schools
(c) Laboratories, research centres, government etc.
(d) Individuals
Q2. Answer the following questions in one line :
Q1. What is meant by a diagram?
Answer:
A diagram is a visual representation used to show the connection or relationship between different variables in a simplified pictorial form.
Q2. What is meant by a graph?
Answer:
A graph is a visual tool used to present complex data in a simplified and understandable way, often using statistical techniques. It is especially helpful for displaying continuous frequency data in a clear and organized format.
Q3. What is meant by a bar diagram?
Answer:
A bar diagram is a chart where different categories of data are represented by rectangular bars drawn from a common baseline. The height of each bar corresponds proportionally to the value of the data in that category.
Q4. What is meant by a pie diagram?
Answer:
A pie diagram, also known as a pie chart, is a circular chart that is divided into slices. Each slice represents a portion of the total data, with the size of each slice determined by the proportion of the category it represents.
Q5. What is a data CD?
Answer:
A data CD is a compact disc that contains organized information and statistical data, usually related to macroeconomic indicators. It is typically used by researchers, analysts, and academic institutions for study and analysis.
3. Answer the following questions in brief:
Q1. What is meant by a diagram and for what purpose it is drawn?
Answer:
A diagram is a visual way of presenting collected data in picture form.
It is simple to create and easy to understand, even for those without deep knowledge of statistics.
Though diagrams require proper measurement and scaling, they do not demand advanced statistical skills.
Diagrams are mostly used to represent discrete (non-continuous) data like:
Number of children born each month,
Prices in rupees,
Number of road accidents, etc.
Q2. What is meant by a graph and for what purpose it is drawn?
Answer:
A graph is a visual tool used to represent statistical data, especially when the data is complex and not self-explanatory.
Understanding and drawing graphs usually requires a basic understanding of statistics.
Graphs are suitable for continuous frequency distributions, such as:
Income-based classification of individuals,
Categorization of students according to their marks.
Q3. State the importance of diagrams and graphs in economics.
Answer:
Diagrams and graphs are important in economics for many reasons:
They help simplify complex concepts and reduce confusion, making economics easier to learn.
Changes in economic indicators over time can be easily visualized using graphs or diagrams.
They assist in understanding developments across various economic sectors.
They allow for quick comparison between groups, regions, or time periods.
These visual tools save time and effort for both teachers and students in explaining and understanding difficult topics.
Complex topics like demand and supply changes, elasticity, or trends in macroeconomic indicators become clearer through visual representation.
Q4. How is computer technology used in the process of learning?
Answer:
Computer technology plays a major role in modern economic studies through various digital tools:
Presentations:
PowerPoint makes it easier to explain economic theories and data using slides, charts, and summaries.
For example, the government budget can be effectively explained using a short presentation with key figures and visuals.
Excel Worksheets:
Economics involves handling large amounts of data, which Excel can manage efficiently.
It helps in calculating totals, averages, regional outputs, exports, etc., and also creates charts in one click.
Graphs and Diagrams:
Programs like MS Word and Excel offer tools to draw curves like demand and supply, or to create graphs and reports.
These help in preparing economic analysis and reports more effectively.
Data Storage:
Economic research involves storing large study materials, which can be saved in digital formats like hard drives, pen drives, CDs, and cloud storage (e.g., Google Drive, Dropbox).
This makes the material portable, safe, and accessible from anywhere.
Advanced Tools:
For handling very large datasets, advanced statistical software like SPSS, SHAZAM, E-Views, and SAS are used (mostly by research institutions due to their high cost).
Free alternatives such as Gretl, PSPP, and R are also available and capable of similar analysis.
Many of these tools are now accessible on smartphones and tablets, increasing flexibility in learning and data handling.
Q5. Write a note on data CD.
Answer:
Various government departments and research agencies collect and compile data on major economic indicators.
These datasets are stored in compact discs (CDs) and made available in the market for research and academic purposes.
Educational institutions and researchers use them for in-depth analysis.
Examples of such data CDs include:
National Income Accounts of India,
Census of India,
Annual Survey of Industries,
NSSO data.
Organizations like CMIE (Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy) also prepare and sell such data in CD form or as software. These are usually bought by research institutions and companies due to their high cost.
Additionally, various ministries also release data CDs. For example, the education department may provide CDs with information about schools and student enrollment in Gujarat. These CDs help store and access vital economic and social statistics in digital form for long-term use.
Q1. State the important aspects to be considered while drawing a diagram and a graph.
Answer:
Key aspects to keep in mind while creating diagrams or graphs are:
Choosing the right type: Select the most appropriate type of diagram or graph based on the nature of data. For instance, a bar chart might suit better than a pie chart in certain cases.
Clarity and neatness: The image should be visually clear and easy to understand. Use of different colors or patterns can help distinguish different parts.
Appropriate scale: The scale should match the data to ensure that the graph or diagram is accurately sized.
Labeling the axes: Both the X-axis and Y-axis must be clearly labeled with the correct variables they represent.
Including data source and table: The original data table and the source from where data is taken should be presented along with the visual. This increases trustworthiness.
Method of data calculation: If any transformation or calculation is done on the original data (like converting values into percentages), a brief explanation of the method or formula used should be mentioned.
Q2. State the important aspects to be considered while drawing a bar diagram.
Answer:
The width of bars should be uniform as it does not reflect data values.
The height or length of bars must accurately represent the values they stand for.
Equal spacing must be maintained between all bars and also between the first bar and the origin point.
Bars should sit on the same baseline, usually aligned with the X-axis. Today, horizontal bars are also commonly used with digital tools.
Bars must be drawn in the same sequence as the data series, starting from left to right. The first data point should be placed closest to the origin.
Q3. Give the difference between diagrams and graphs.
Answer :
| Diagram | Graph |
|---|---|
| Can be made without deep knowledge of statistics. | Requires good understanding of statistical methods. |
| Used for data with discrete (non-continuous) values. | Used for data with continuous values. |
| Suitable for presenting information to the general public. | Not suitable for general audience; meant for experts. |
| Easy to draw and interpret. | More complex to create and understand. |
| Examples: Pictographs, bar charts, pie charts. | Examples: Time-series graphs, histograms, cumulative frequency graphs, etc. |
Q4. Explain the usefulness of internet technology in the process of learning.
Answer:
The internet, being a digital medium, supports education in many ways, especially in economics:
Tutorials: Several educational platforms provide PowerPoint slides, worksheets, and explanations freely. These can be used to learn topics like statistical tools or economic theories.
Active learning: Online video lectures and live sessions by experts allow students to learn topics just like in a classroom environment.
Reading resources: A variety of free e-books, journals, and research articles are available online. Some are accessible through paid subscriptions too.
Information gathering: The internet helps in finding academic details, such as courses, universities, or economic events, with just a few clicks.
Additional support: Quotes, book references, and other study aids are easily searchable online.
Data access: Economics uses a lot of secondary data which is available on official websites of bodies like RBI, Ministry of Finance, CSO, WHO, World Bank, etc. These sites provide authentic and updated statistics for analysis and reference.
Q5. Give the caution areas in using computer and internet technologies for studying.
Answer:
Computers and the internet are useful tools for learning, but they are not actual study materials. They help us study faster and better, but they cannot replace our own learning or understanding.
We must know how to use computers properly. Also, we should learn how to use statistical tools and software in the right way. Computers follow the commands we give, so if we give wrong data or wrong formulas, we might get incorrect results or even lose our work.
While using the internet for study, we should be careful of the following things:
Internet is just a tool. It cannot take the place of teachers, books, or our own thinking.
Many websites have fake, wrong, or copied content. We should not use such material.
We should always check if the information is true and from a good source.
Always use study material and data from trusted and official websites.
So, we must use computers and the internet wisely and carefully while studying.
Q 6. What is the importance of diagrams and graphs in context of presenting information about economics for lay persons and for experts.
Answer:
Economics studies and explains real-world events using large amounts of data, which can be complex. To simplify this, data is often shown through pictures like diagrams and graphs. These help in better understanding of concepts.
Diagrams are very useful for the general public. They are simple to draw and easy to interpret, even without deep knowledge of statistics. So, when economic information is shown through diagrams, it attracts more interest from non-experts.
Graphs, however, are used for deeper statistical understanding and are meant for experts or researchers. They are used in advanced studies and research to analyze data trends, relationships, and patterns.
In short, diagrams help the general audience understand economics easily, while graphs help scholars and researchers in analyzing data effectively.
5. Answer the following questions in detail :
Q.1 Explain the types of diagrams in detail.
Answer:
There are different types of diagrams used to represent data. Let’s understand them one by one:
(1) Time-Based Line (Curve) Diagram:
This type of diagram is used when data is related to time.
For example: price of a share over 30 days, number of vehicles passing a junction each hour, or population growth from 1951 to 2001.
It shows the relationship between two variables and how one changes over time.
Usually, time (independent variable) is shown on the X-axis and the other variable (dependent variable) is shown on the Y-axis.
In economics, line diagrams are often used to show demand and supply curves.
(2) Bar Diagram:
A bar diagram uses bars to represent and compare data across different categories. Bars can be drawn vertically or horizontally.
Purpose:
It shows how values of a variable are distributed across categories.
For example: literacy rate in different years or among males and females.
Each bar represents a section, and the height or length of the bar shows the value of that section.
Comparing bar heights/lengths helps us understand the differences between values.
Types of Bar Diagrams:
Bar diagrams are mainly of three types:
(A) Simple Bar Diagram:
It shows the values of one variable across categories.
For example, sales data across different regions or months.
The difference in bar lengths helps us easily compare the data.
(B) Clustered Bar Diagram:
This diagram shows data for more than one group under the same category.
For example, comparing sales from two branches of a store over a period of time.
Each group is shown with separate bars placed together (clustered), often using different colors or patterns.
Another example is comparing male and female literacy for different years.
(C) Divided Bar Diagram:
Here, each bar is divided into parts to show different components of a total.
It shows subdivisions within each category.
For example, total population divided into rural and urban groups.
Different colors are used for each segment, and values are written on each part for clarity.
(3) Pie Diagram (Circle Chart):
A pie diagram is a circular chart divided into slices, where each slice represents a part of the total data.
The entire circle equals 360°, and each slice is sized based on its proportion of the total.
It is best used when you want to show how different sections make up a whole.
Pie diagrams can be used in place of bar diagrams for similar kinds of data.
Formula to Calculate Degree for Each Slice: