Compare and demonstrate with examples the different types of command redirection and piping in Linux.
SOLUTION....
🔹 1. Command Redirection
In Linux, redirection is used to control where the input and output of a command go (file, screen, or another command).
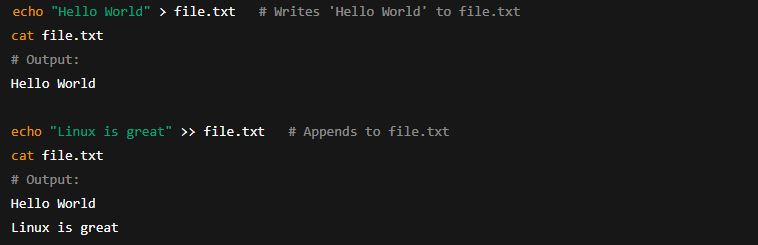
(a) Standard Output Redirection (> and >>)
>: Redirects output to a file (overwrites).>>: Redirects output to a file (appends).
Example:
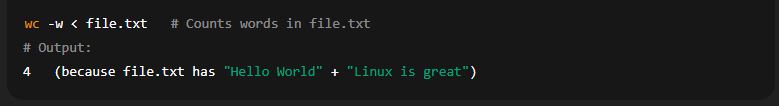
(b) Standard Input Redirection (<)
Takes input for a command from a file instead of keyboard.
Example:
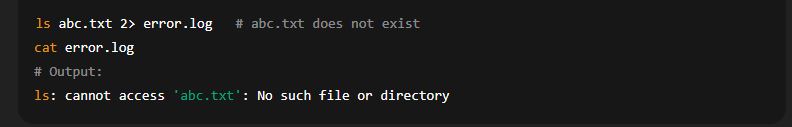
(c) Standard Error Redirection (2>, 2>>)
Redirects error messages to a file.
Example:
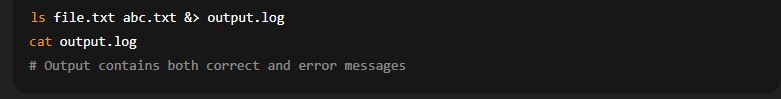
(d) Redirect Both Output and Error (&> or > file 2>&1)
Redirects both stdout and stderr to the same file.
Example:
(e) Here Document (<<)
Redirects a block of text to a command.
Example:

(f) Here String (<<<)
Redirects a single string as input.
Example:

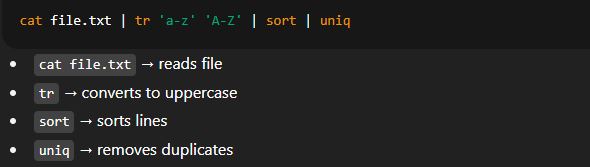
🔹 2. Piping (|)
A pipe (
|) sends the output of one command as input to another command.
Example:

Multiple Pipes
Example: