Describe in detail how to validate forms in AngularJS.
SOLUTION
Form Validation in AngularJS
Form validation is the process of checking whether the data entered by a user is correct, complete, and acceptable before submitting it. AngularJS makes form validation easier by providing built-in directives, CSS classes, and properties that help in real-time validation.
1. AngularJS Form and Input Controls
In AngularJS, forms are created using the <form> tag, and input controls are created using elements like <input>, <select>, and <textarea>.
Each form and input can have a name that AngularJS uses to track their state.
Example:
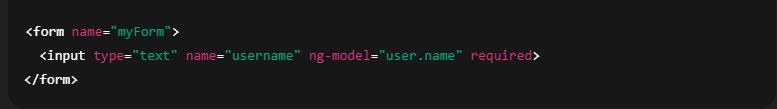
2. Built-in Directives for Validation
AngularJS provides several attributes to validate user input:
required – Ensures that a field must not be empty.
<input type="text" ng-model="user.name" required>ng-minlength / ng-maxlength – Validates length of text.
<input type="text" ng-model="user.password" ng-minlength="6" ng-maxlength="12">ng-pattern – Matches the input against a regular expression (useful for emails, phone numbers, etc.).
<input type="text" ng-model="user.email" ng-pattern="/^[a-z0-9._%+-]+@[a-z0-9.-]+\.[a-z]{2,4}$/">type=”email/number/url” – Provides automatic HTML5-based validation.
<input type="email" ng-model="user.email" required>novalidate – Used on the
<form>tag to disable default HTML5 validation, letting AngularJS handle it instead.
3. Form States and CSS Classes
AngularJS automatically assigns CSS classes to input fields depending on their state. These classes help in applying styles and showing messages.
ng-valid → Input is valid.
ng-invalid → Input is invalid.
ng-dirty → User has modified the input.
ng-pristine → Input has not been touched yet.
ng-touched → Input field was clicked or focused.
Example with CSS:

4. Checking Form Status
AngularJS allows checking form and input properties such as:
myForm.$valid → Returns
trueif all inputs are valid.myForm.$invalid → Returns
trueif any input is invalid.myForm.$pristine → Returns
trueif form is untouched.myForm.$dirty → Returns
trueif user modified any field.
Example:

5. Displaying Error Messages
Error messages can be displayed conditionally using ng-show or ng-if.
Example:
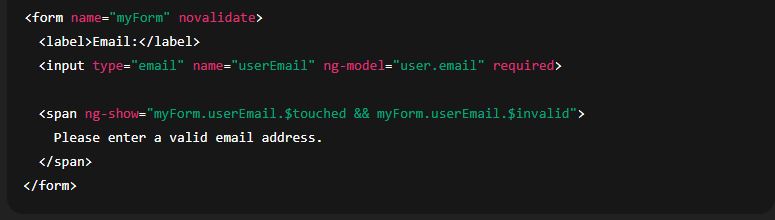
6. Example: Complete Form Validation
<div ng-app=”myApp” ng-controller=”myCtrl”>
<form name=”myForm” novalidate>
<p>
Name: <input type=”text” name=”username” ng-model=”user.name” required>
<span ng-show=”myForm.username.$touched && myForm.username.$invalid”>
Name is required.
</span>
</p>
<p>
Password: <input type=”password” name=”password” ng-model=”user.password” ng-minlength=”6″>
<span ng-show=”myForm.password.$touched && myForm.password.$error.minlength”>
Password must be at least 6 characters.
</span>
</p>
<p>
Email: <input type=”email” name=”email” ng-model=”user.email” required>
<span ng-show=”myForm.email.$touched && myForm.email.$invalid”>
Enter a valid email.
</span>
</p>
<button ng-disabled=”myForm.$invalid”>Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module(“myApp”, []);
app.controller(“myCtrl”, function($scope) {
$scope.user = {};
});
</script>
7. Summary
AngularJS makes form validation dynamic and real-time using directives like
required,ng-pattern, andng-minlength.Input fields are automatically tracked with states (
$valid,$invalid,$dirty, etc.).Error messages and CSS styles help guide users.
Validation prevents invalid data submission and improves user experience.
