Explain extract and write commands for csv and excel files using Dataframe.
SOLUTION....
Pandas is a powerful Python library used for data manipulation and analysis. One of its most useful features is handling structured data stored in CSV (Comma-Separated Values) and Excel files. Pandas provides built-in methods to easily read (extract) and write (save) these files.
1. Extracting (Reading) CSV files
We use pd.read_csv() to load data from a CSV file into a DataFrame.
Example:

🔹 Here:
"students.csv"is the file name.The function reads the file and stores the content in
df(a DataFrame)..head()shows the first 5 rows for quick preview.
2. Writing (Saving) CSV files
We use DataFrame.to_csv() to save a DataFrame into a CSV file.
Example:

🔹 Here:
"output.csv"is the new file name.index=Falseprevents Pandas from writing row numbers into the file.
3. Extracting (Reading) Excel files
We use pd.read_excel() to read data from an Excel file (.xls or .xlsx).
This requires the openpyxl library for .xlsx files.
Example:
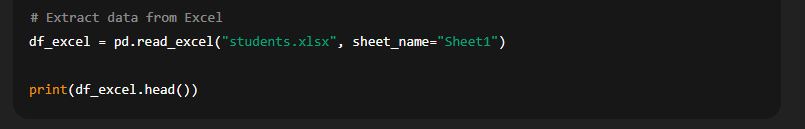
🔹 Here:
"students.xlsx"is the Excel file.sheet_namespecifies which worksheet to read.
4. Writing (Saving) Excel files
We use DataFrame.to_excel() to export a DataFrame into an Excel file.
Example:
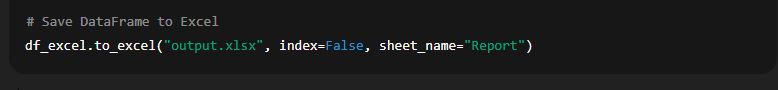
🔹 Here:
"output.xlsx"is the exported file.sheet_name="Report"names the worksheet.index=Falseavoids saving row numbers.
