Querying and SQL Functions

ASSIGNMENT
NOTES
🌐 Relational Data Model – Explained in Detail.
The Relational Data Model is a way of organizing data into tables (also called relations). It was introduced by E.F. Codd in 1970 and is widely used in modern database systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server.
🔹 Key Concepts of the Relational Data Model
Relation (Table)
A relation is a table that contains data in rows and columns.
Each row is called a tuple, and each column is called an attribute.
Example:
ASTUDENTStable with columns:Roll_No,Name,Age,Class.
Attribute (Column)
Attributes are the properties or fields of a table.
Each attribute has a data type (like integer, string, date).
Example:
Nameis a string type attribute in the STUDENTS table.
Tuple (Row)
A tuple is a single record in the table.
Each row contains data about one instance.
Example: A row in the STUDENTS table may be (101, “Ravi”, 17, “12A”).
Domain
A domain is the set of valid values an attribute can take.
For example, the domain of the
Ageattribute might be from 1 to 100.
Degree and Cardinality
Degree: Number of attributes (columns) in a relation.
Cardinality: Number of tuples (rows) in a relation.
🔹 Types of Keys in Relational Model
Primary Key
Uniquely identifies each record in a table.
Cannot be null and must be unique.
Candidate Key
A field or set of fields that could qualify as a primary key.
Foreign Key
An attribute in one table that refers to the primary key in another table.
Used to create a relationship between tables.
Composite Key
A key made up of two or more attributes to uniquely identify a tuple.
🔹 Relational Integrity Rules
Entity Integrity
The primary key must have a unique value and cannot be null.
Referential Integrity
A foreign key must match an existing value in the referenced table or be null.
🔹 Advantages of Relational Data Model
Simple Structure: Easy to understand and use.
Data Integrity: Maintains accuracy and consistency.
Flexibility: Tables can be easily updated and queried.
Scalability: Suitable for small and large datasets.
✅ What is SQL?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language.
It is a standard language used to communicate with relational databases.
🔹 Key Uses of SQL:
Create and manage tables
Insert, update, and delete data
Retrieve data using queries
Filter, sort, and aggregate information
Manage users, permissions, and database structures
🔹 Common SQL Commands:
| Command | Purpose | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREATE | To create tables or databases | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INSERT | To add new records | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SELECT | To retrieve data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UPDATE | To modify existing data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DELETE | To remove data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DROP | To delete tables or databases | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ALTER | To
Classification of SQL StatementsSQL (Structured Query Language) statements are divided into several categories based on their purpose. Each category is used for a specific type of operation in a relational database. 🔹 1. Data Definition Language (DDL)These statements are used to define and modify the structure of database objects such as tables, schemas, indexes, and views.
🔹 2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)These statements deal with managing the actual data in the database. DML is used to add, modify, and delete records.
🔹 3. Data Query Language (DQL)This category is used for retrieving data from the database. It helps in filtering, sorting, and analyzing data.
🔹 4. Data Control Language (DCL)These statements are used to control access to the data in the database. DCL helps manage user permissions and data security.
🔹 5. Transaction Control Language (TCL)TCL statements are used to manage transactions in the database. Transactions are a group of SQL operations that should be executed together.
✅ What is MySQL?MySQL is a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) that uses SQL as its language. 🔹 Key Features of MySQL:
Common MYSQL Data Types.In MySQL, data types define the kind of value that can be stored in a column. Choosing the correct data type is essential for data accuracy, storage efficiency, and performance. MySQL data types are broadly categorized into:
🔹 1. Numeric Data TypesThese are used to store numbers—both whole numbers and decimal numbers.
🔹 2. String (Character) Data TypesThese store text, words, or characters.
🔹 3. Date and Time Data TypesUsed to store dates, times, or a combination of both.
🔹 4. Other Special Data Types
✅ 1. Creating a Database in MySQLA database is a collection of related tables used to store structured information. 🔹 SQL Command: 🔍 Explanation:
TRY THIS✅ 2. Accessing (Using) a DatabaseBefore creating tables or inserting data, you must select the database you want to work with. 🔹 SQL Command: TRY THIS🔍 Explanation:
✅ 3. Creating a Table in MySQLTables hold data in rows and columns. You must define the table structure with column names and data types. 🔹 SQL Command: 🔍 Explanation:
TRY THIS✅ 4. Inserting Data into a TableOnce the table is created, you can add rows of data using the 🔹 SQL Command: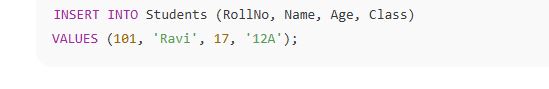 🔍 Explanation:
TRY THIS🔄 Insert Multiple Rows: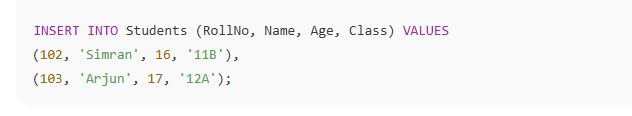 TRY THISMaking Simple Queries through Select CommandThe 🔹 1. Basic SELECT QuerySyntax: 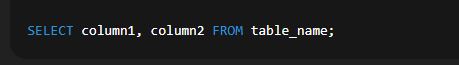 Explanation:
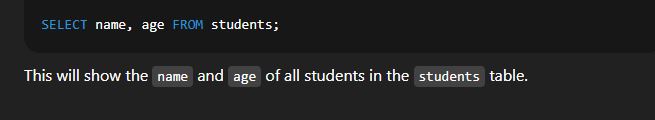 🔹 2. Selecting All ColumnsSyntax:  Explanation:
Example: 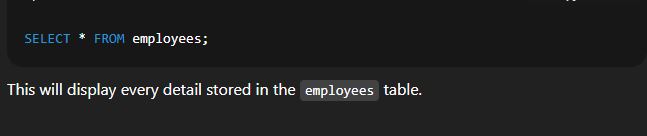 🔹 3. Using WHERE Clause to Filter DataSyntax: 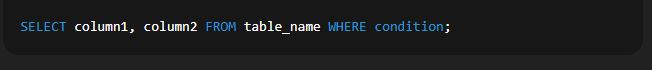 Explanation:
Example: 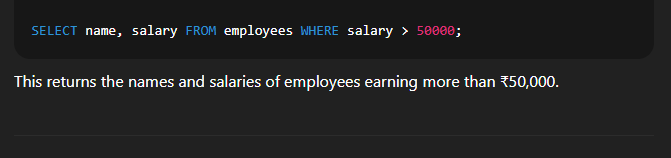 🔹 4. Using Aliases with AS KeywordSyntax: 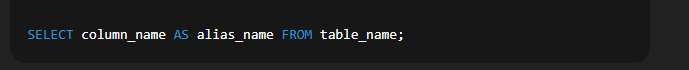 Explanation:
Example: 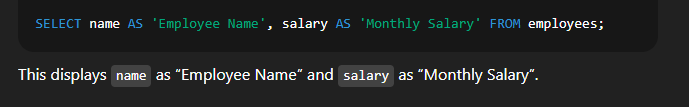 🔹 5. Using DISTINCT to Avoid Duplicate RowsSyntax: 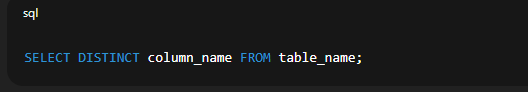 Explanation:
Example: 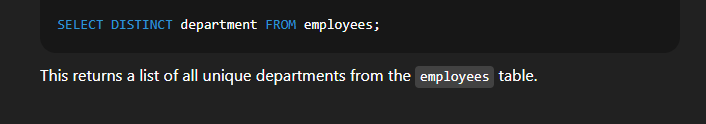 🔹 6. Using ORDER BY to Sort the OutputSyntax: 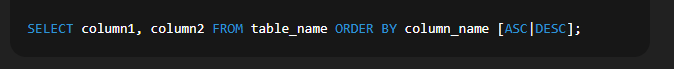 Explanation:
Example: 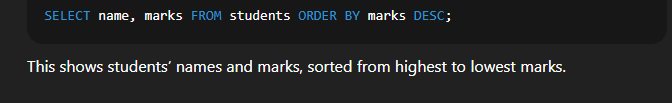 🔹 7. Using LIMIT to Restrict the Number of RowsSyntax:  Explanation:
Example: 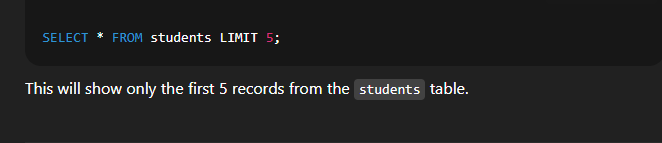 🔹 8. Combining Multiple Conditions with WHERE, AND, ORSyntax:  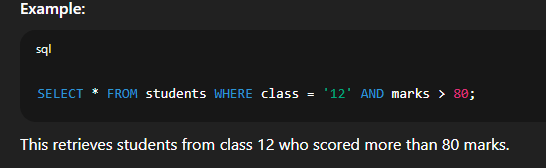 🔹 9. Using IN to Match Multiple ValuesSyntax:  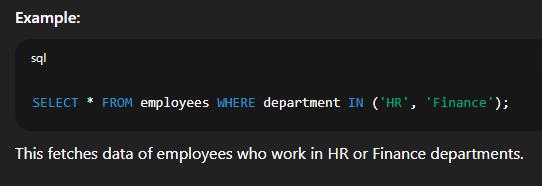 🔹 10. Using BETWEEN for Range FilteringSyntax:  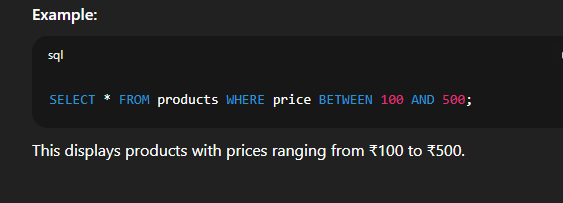 📘 Creating Table with SQL ConstraintsWhen you create a table in SQL, you can apply constraints to control the validity, uniqueness, and integrity of the data stored in that table. Constraints help ensure that data entered into a table follows certain rules. 🔹 What is a SQL Constraint?A constraint is a rule that limits the type of data that can be stored in a column. Constraints are applied at the column level or table level while creating or modifying tables. 🔹 Common SQL Constraints
✅ 1. Creating Table with NOT NULL Constraint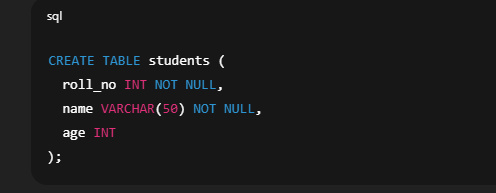 Explanation:
✅ 2. Creating Table with UNIQUE Constraint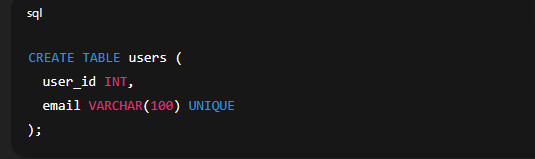 Explanation:
✅ 3. Creating Table with PRIMARY KEY Constraint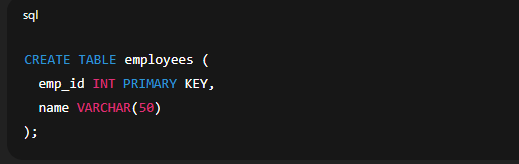 Explanation:
✅ 4. Creating Table with FOREIGN KEY Constraint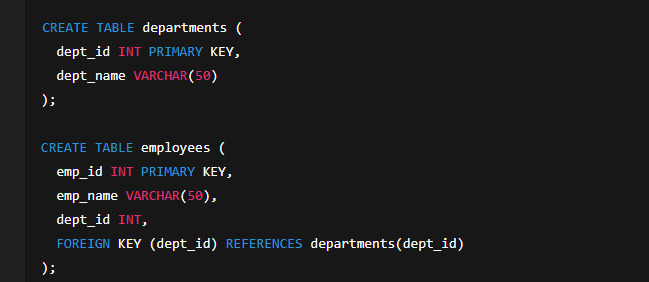 Explanation:
✅ 5. Creating Table with CHECK Constraint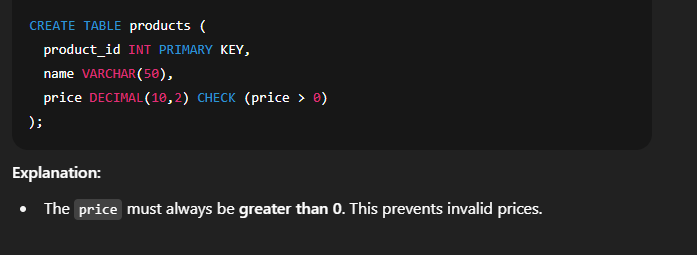 ✅ 6. Creating Table with DEFAULT Constraint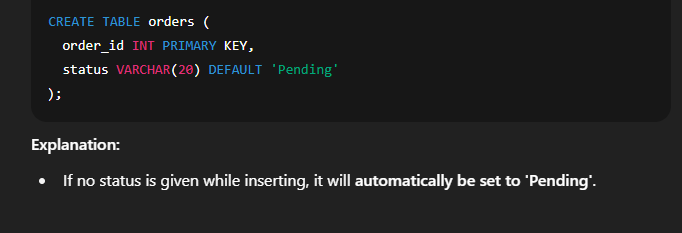 🔸 Combining Multiple Constraints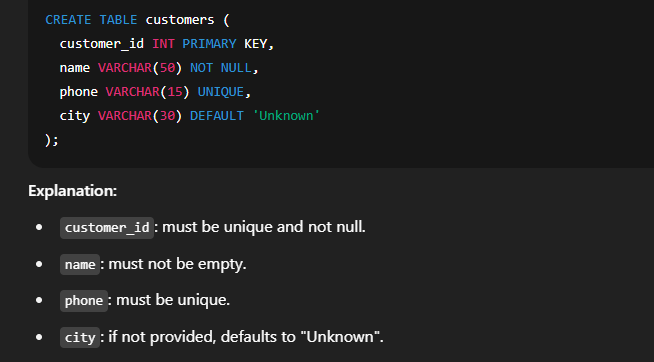 🔹 SQL Constraint Types Overview
📘 Inserting Data into Another Table in SQLIn SQL, you can copy data from one table to another using the 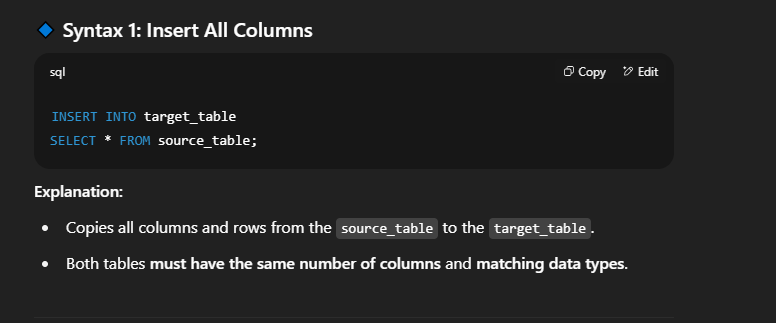 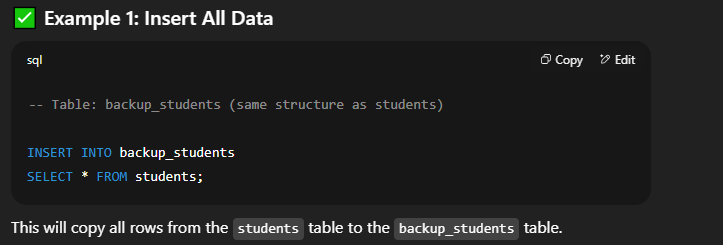 🔹 Syntax 2: Insert Selected Columns Only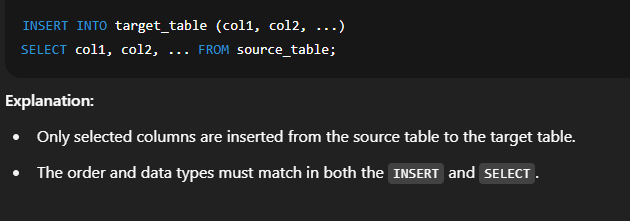 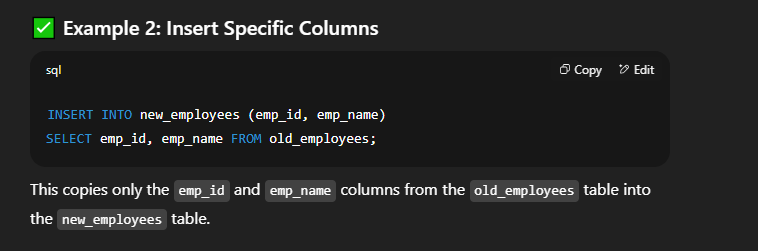 🔹 Syntax 3: Insert with Conditions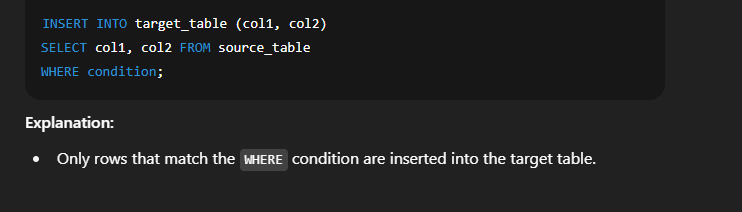 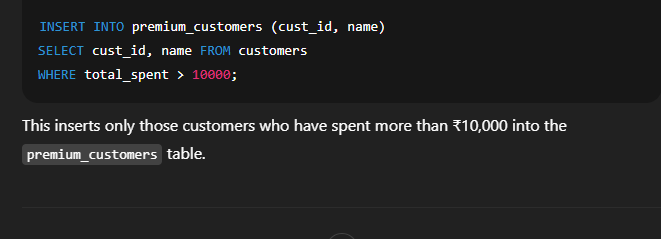 🔸 Important Points to Remember
🔹 Example with Missing Columns (Error)Suppose the target table has 3 columns ( 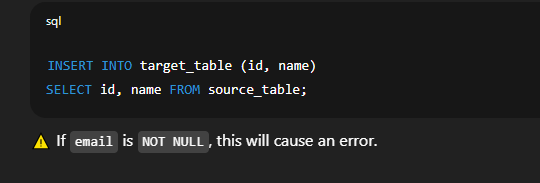 📘 Modifying Data in a Table in SQLIn SQL, we use the 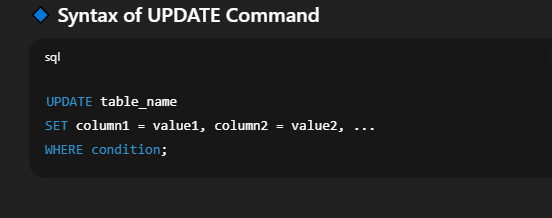 🔍 Explanation of Syntax:
⚠️ Without a 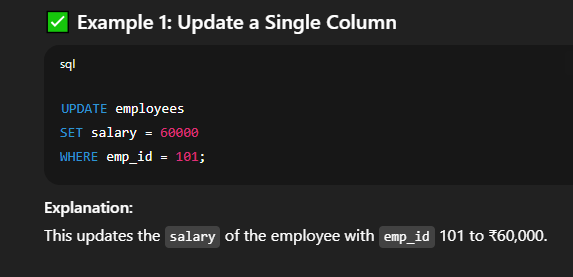 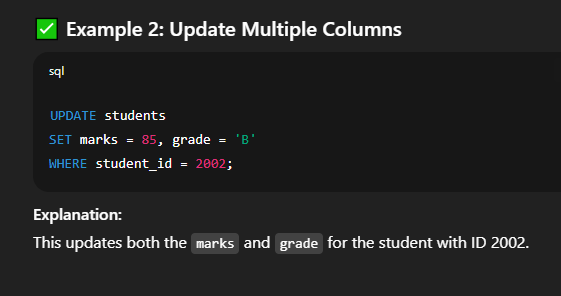 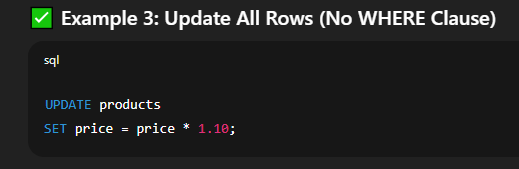 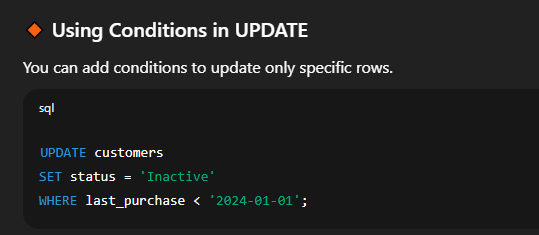 🔐 Important Tips and Warnings⚠️ SQL UPDATE Tips & Warnings
📘 Modifying Data in a Table in SQLIn SQL, we use the 🔹 Syntax of UPDATE CommandUPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...
WHERE condition;🔍 Explanation of Syntax:
⚠️ Without a 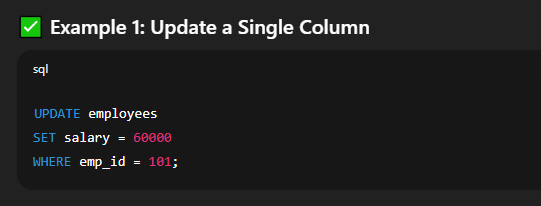 Explanation: 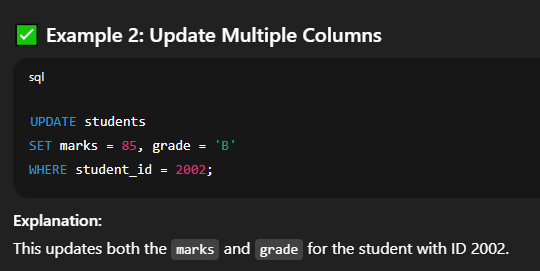 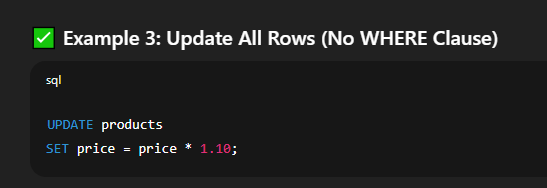 Explanation: 🔸 Using Conditions in UPDATEYou can add conditions to update only specific rows. 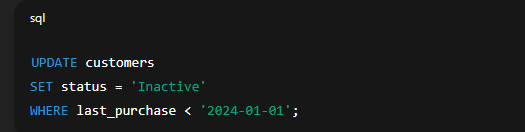 🔐 Important Tips and Warningssign up!
We’ll send you the hottest deals straight to your inbox so you’re always in on the best-kept software secrets.
|
